Introducing Solar Scan
A solar potential assessment tool powered by AI.
Introduction
Solar energy has been growing rapidly in The Netherlands. However, its potential is still underexplored when compared to other renewable energy sources, and this fact makes it an interesting alternative to explore. Furthermore, solar is also easy to adopt at the residential level and is accessible to most of the population.
I'd put my money on the sun and solar energy. What a source of power! I hope we don't have to wait until oil and coal run out before we tackle that. -Thomas Edison
One key action for the promotion of residential solar photovoltaic (PV) energy is the assessment of the solar potential. Assessing solar potential allows identifying the best locations where solar panels can be installed. We introduce Solar Scan, a tool that will help in assessing the solar potential in The Netherlands. Solar Scan uses satellite imagery data and information extracted from the CBS database.
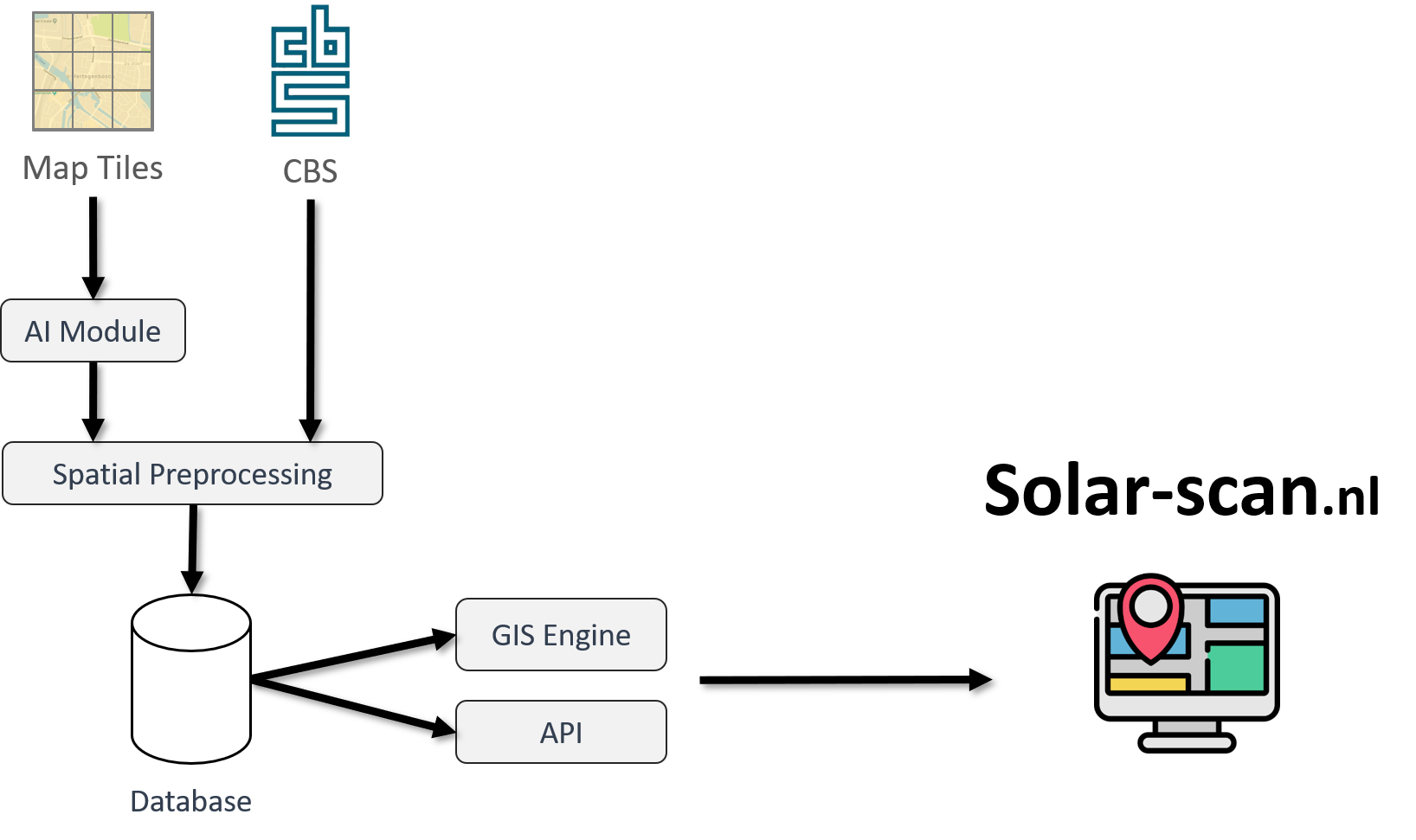
Solar Scan is composed of several modules that work seamlessly and process the data, including an AI engine and a spatial processing pipeline.
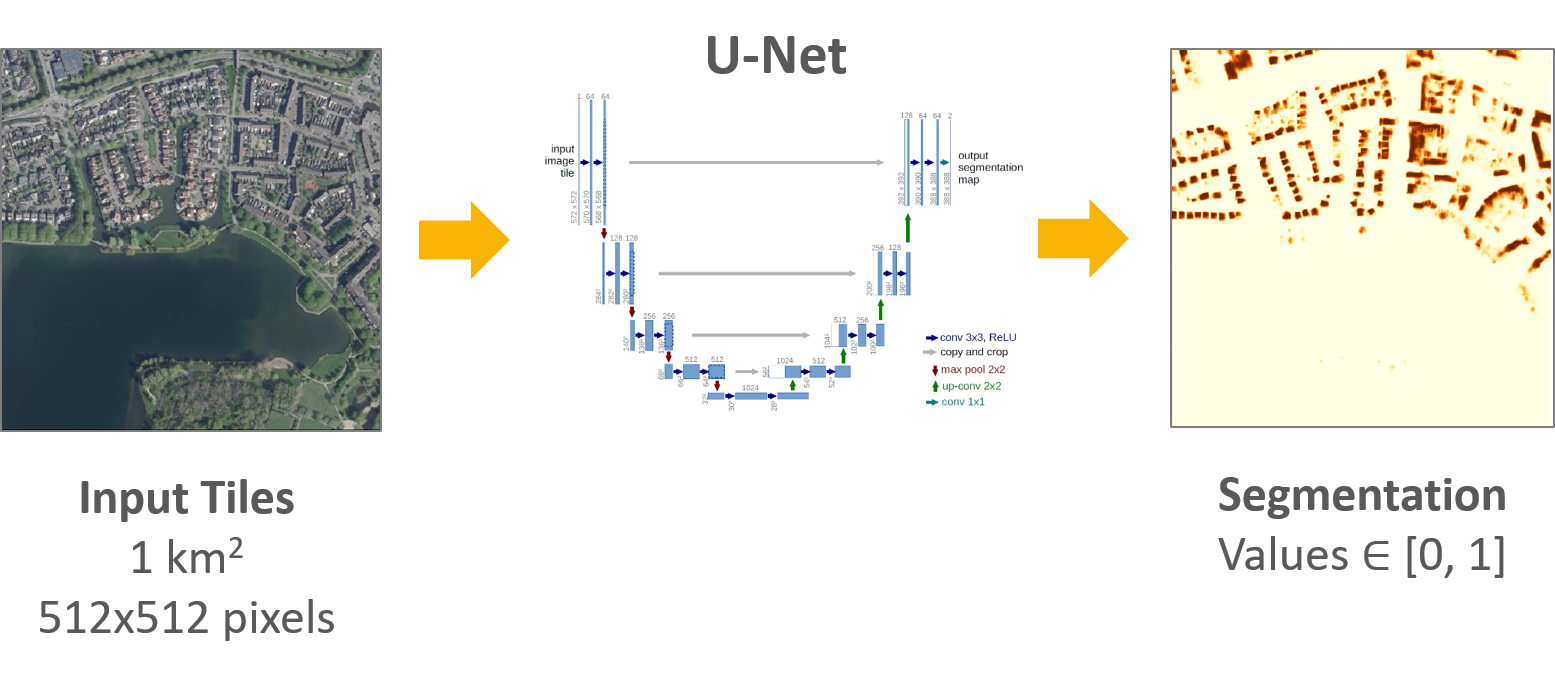
AI Power
Solar Scan is powered by an AI module whose output is used for solar potential assessment. This module uses a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) to segment the building’s rooftops from satellite images and estimates the useful area available for installing solar panels. The neural architecture applied for segmentation is U-Net, which achieves state-of-the-art performance in many complex image segmentation tasks. The model was trained in a supervised fashion on a dataset containing map tiles and the corresponding segmented images. We trained it from scratch on CoLab, using accelerated hardware (GPU), during 50 training epochs.
Spatial Processing Pipeline
The CBS data extracted, and the rooftop segmentation output, are displayed on a map integrated in a web application.
To do so, we developed a spatial processing pipeline that consisted of the following steps:
- Built a grid of polygons covering the area to be represented and associated them with their center coordinates.
- Stored the CBS information and the segmentation results in a spatial database.
- Assigned the spatial data in the database to the corresponding polygons.
- Set a Geographical Information System (GIS) engine to process the spatial data.
- Rendered the spatial data on an interactive map.
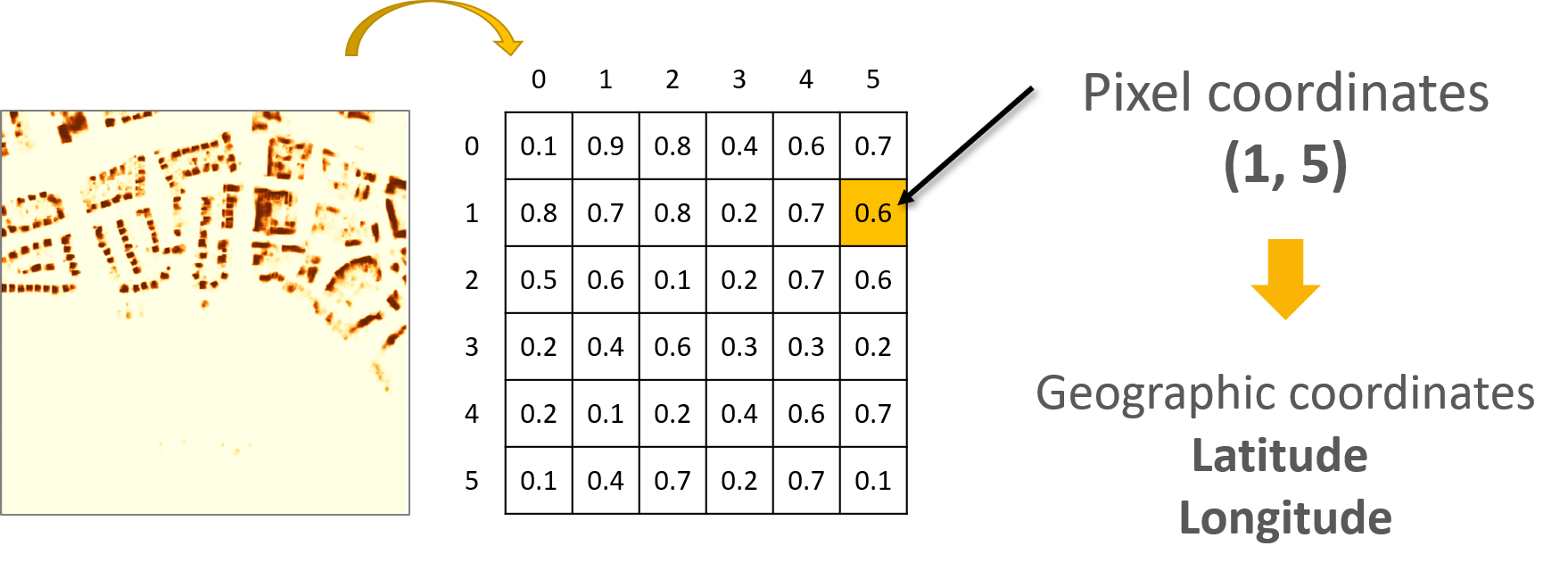
With this spatial data processing pipeline, we aim to have a platform in place to investigate and assess the solar potential in different geographical areas. For this purpose, we thought about developing two elements: an interactive map and a solar information summary associated with the viewed area on the map. We represent the CBS data extracted on the map. In addition, we use the rooftop’s segmentation as a basis to compute metrics that provide insights on the solar potential in the viewed area.
The map includes multiple layers, showing the solar information aggregated in hexagon shapes. Each hexagon contains one or more neighborhoods. The information regards the number of solar panels installed, the power currently generated by solar panels, and a detailed view of the potential rooftops.
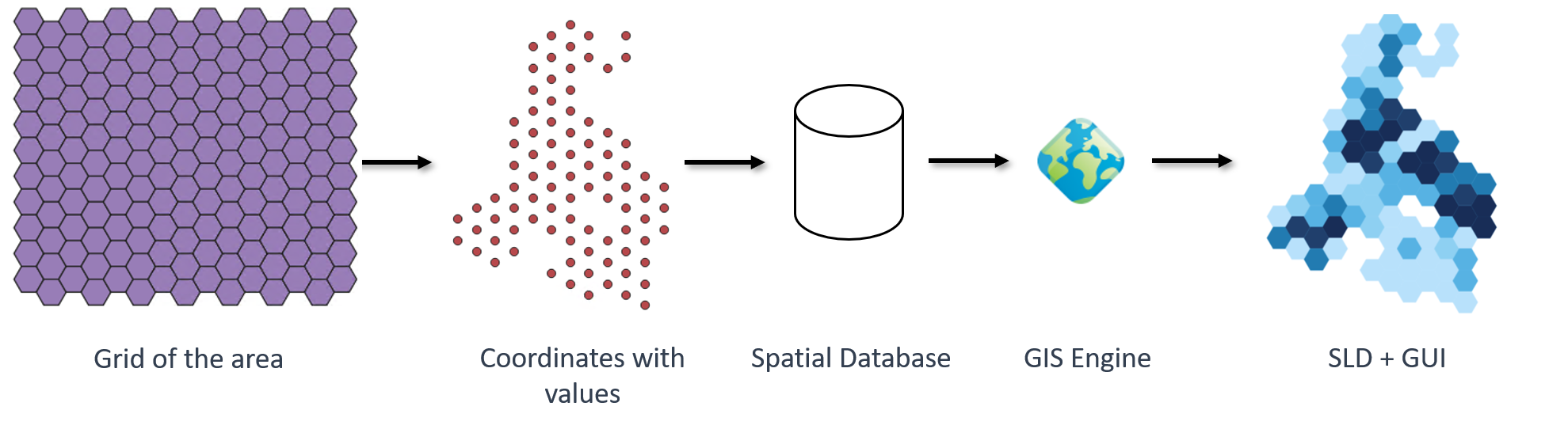
The CBS data extracted, and the rooftop segmentation output, are displayed on a map integrated in a web application.
The segmentation of satellite images, performed using a deep learning model, allows us to estimate the rooftop area available, in square meters, for a given view area. Based on this estimation, we compute several solar metrics that provide valuable insights useful for solar potential assessment. Specifically, we compute the following solar metrics:
- Number of solar panels installed.
- Available area for installing solar panels.
- Potential energy generation.
- Money savings for one year of generation.
- Solar potential index.
Solar Scan includes a representation of the rooftop’s segmentation on an interactive map, as well as the solar insights computed for the viewed area, shown on the right side.
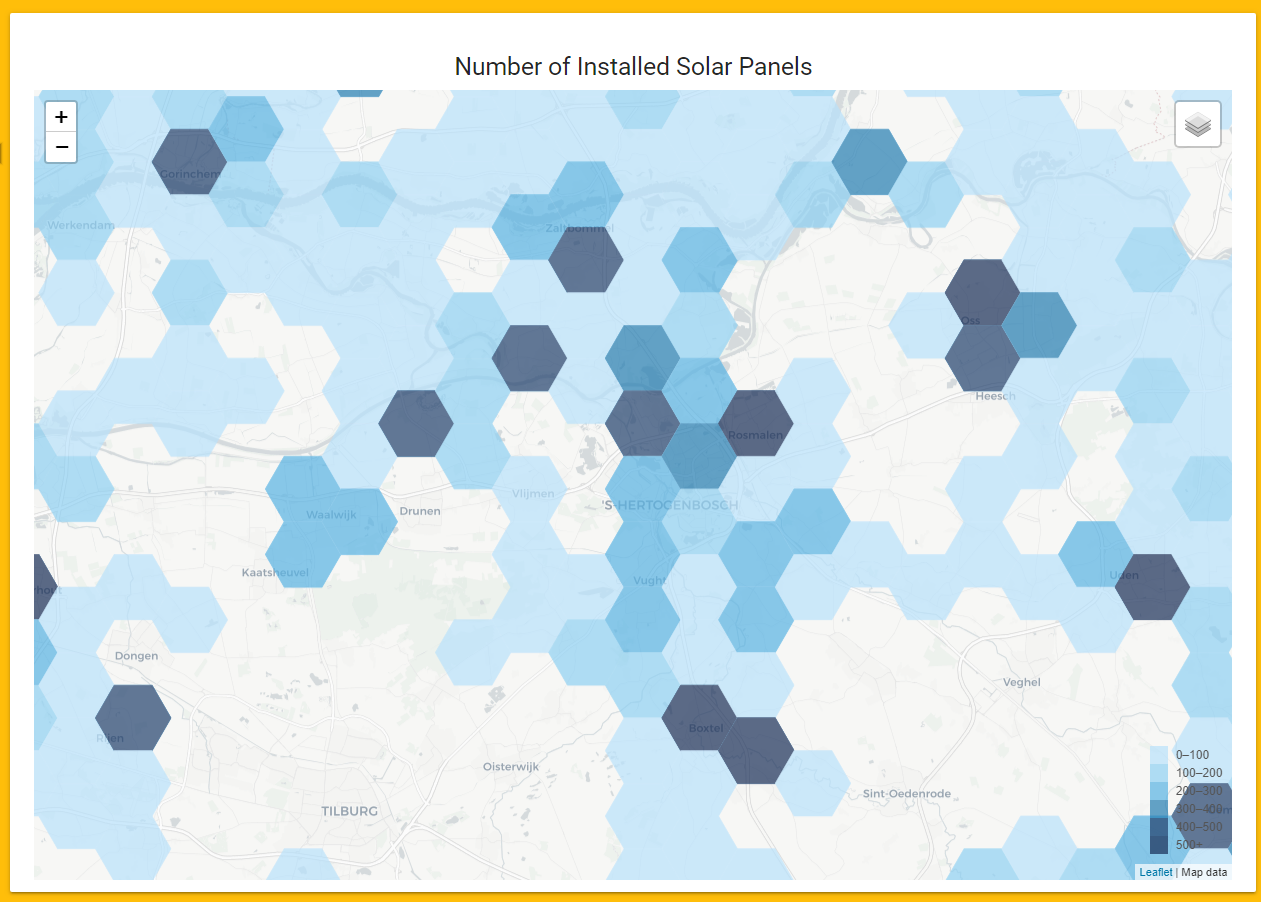
We designed, implemented and deployed a solution that provides two benefits for our individual or professional target users. Solar Scan helps users to grasp the current situation on solar panels already installed across neighborhoods. In addition, they are able to investigate the solar energy potential in a specific neighborhood.
Solar Scan includes a representation of the rooftop’s segmentation on an interactive map, as well as the solar insights computed for the viewed area, shown on the right side.
We wish you like Solar Scan as much as we do!